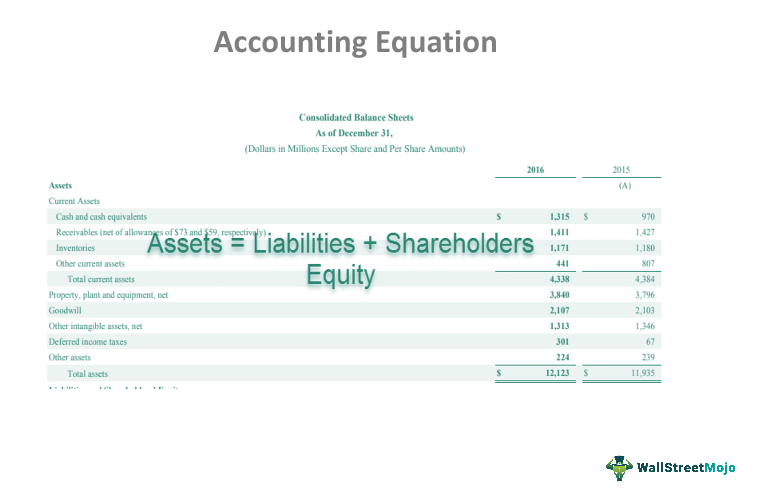
Valid financial transactions always result in a balanced accounting equation which is the fundamental characteristic of double entry accounting (i.e., every debit has a corresponding credit). The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity. For example, if the total liabilities of a business are $50K and the owner’s equity is $30K, then the total assets must equal $80K ($50K + $30K).
Effects of Transactions on Accounting Equation
- The balance sheet reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s (or stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time.
- (Note that, as above, the adjustment to the inventory and cost of sales figures may be made at the year-end through an adjustment to the closing stock but has been illustrated below for completeness).
- The balance sheet is also known as the statement of financial position and it reflects the accounting equation.
- For example, if a business signs up for accounting software, it will automatically default to double-entry.
Understanding how the accounting equation works is one of the most important accounting skills for beginners because everything we do in accounting is somehow connected to it. The global adherence to the double-entry accounting system makes the account-keeping and -tallying processes more standardized and foolproof. Think of retained earnings as savings, since it represents the total profits that have been saved and put aside (or “retained”) for future use. The major and often largest value assets of most companies are that company’s machinery, buildings, and property. It will always be true as long as all transactions are appropriately accounted for and can never fail or be out of balance for any given entity.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
On the other hand, equity refers to shareholder’s or owner’s equity, which is how much the shareholder or owner has staked into the company. Small business owners typically have a 100% stake in their company, while growing businesses may have an investor and share 20%. Once all of the claims by outside companies and claims by shareholders are added up, they will always equal the total company assets. This transaction brings cash into the business and also creates a new liability called bank loan. On the other side of the equation, a liability (i.e., accounts payable) is created.
Arrangement #3: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Capital – Owner’s Drawings + Revenues – Expenses
This statement reflects profits and losses that are themselves determined by the calculations that make up the basic accounting equation. In other words, this equation allows businesses to determine revenue as well as prepare a statement of retained earnings. This then allows them to predict future profit trends and adjust business practices accordingly. Thus, the accounting equation is an essential step in determining company profitability. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced.
Components of the Basic Accounting Equation

The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation. Notice that each transaction changes the dollar value of at least one of the basic elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner’s equity) but the equation as a whole does not lose its balance. The accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity. This shows all company assets are acquired by either debt or equity financing.
Arrangement #1: Equity = Assets – Liabilities
In fact, most businesses don’t rely on single-entry accounting because they need more than what single-entry can provide. Single-entry accounting only shows expenses and sales but doesn’t establish how those transactions work together to determine profitability. While the accounting equation goes hand-in-hand with the balance sheet, it is also a fundamental aspect of the double-entry accounting system.
The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement. If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. As a core concept in modern accounting, this provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced across a given accounting cycle. Equity on the other hand is the shareholders’ claims on the company assets.
This is what ensures that every transaction makes sense and there will always be an entry on both sides of each transaction. The third part of the accounting equation is shareholder equity. The revenue a company shareholder can claim after xero vs quickbooks online review debts have been paid is Shareholder Equity. The accounting equation states that the amount of assets must be equal to liabilities plus shareholder or owner equity. This arrangement is used to highlight the creditors instead of the owners.
These equations, entered in a business’s general ledger, will provide the material that eventually makes up the foundation of a business’s financial statements. This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments. The fundamental accounting equation, also called the balance sheet equation, is the foundation for the double-entry bookkeeping system and the cornerstone of accounting science. In the accounting equation, every transaction will have a debit and credit entry, and the total debits (left side) will equal the total credits (right side).
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
The inventory (asset) will decrease by $250 and a cost of sale (expense) will be recorded. (Note that, as above, the adjustment to the inventory and cost of sales figures may be made at the year-end through an adjustment to the closing stock but has been illustrated below for completeness). As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31.

